Digital signatures confirm document authenticity, integrity, and signer identity across modern electronic workflows. However, many users remain uncertain about verifying signatures correctly within shared PDF files. Online validation tools help users assess whether signed PDFs were altered after approval securely.
This guide explains how to validate a signature in a PDF online using secure verification methods. It clarifies certificate status, trust chains, timestamps, and warning indicators displayed during validation checks. By following structured steps, users confidently interpret results before sharing legally sensitive documents. Furthermore, accurate validation supports compliance, reduces disputes, and strengthens confidence across digital document exchange workflows.

In this article
- What It Means to Validate a Signature in a PDF
- When and Why You Need to Validate a PDF Signature
- How Online PDF Signature Validation Works
- How to Validate a Digital Signature in a PDF Online (General Steps)
- How to Verify a PDF Signature Using Adobe Reader
- What "Valid," "Invalid," and "Unknown" Signature Statuses Mean
- Common Reasons a PDF Signature Fails Validation
- How to Validate a PDF Digital Signature in Detail Using PDFelement
- Online vs. Adobe vs. Desktop Validation: What's the Difference?
Part 1. What It Means to Validate a Signature in a PDF
Signature validation confirms whether a signed PDF can be trusted technically and legally. Many users confuse a visible signature with a verified digital signature process. Understanding this difference is essential for secure document handling across professional digital workflows.
What PDF Signature Verification Actually Checks
PDF signature verification examines the cryptographic data embedded in a digital signature. It checks document integrity, verifies signer certificates, and confirms validity during signing time. This process ensures signatures comply with trusted security standards and verification requirements.
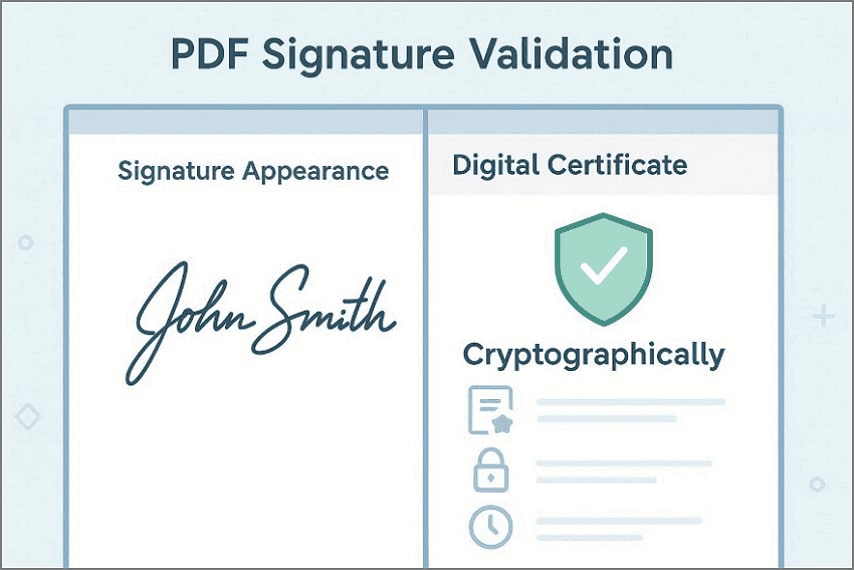
Visible Signature vs. Cryptographically Valid Signature
A visible signature appearance is only a visual marker placed onto the document. It does not verify document integrity, signer identity, or protection against later changes. A cryptographically valid digital signature uses encryption and certificates to prove authenticity. This method reliably detects tampering and supports enforceable trust across systems globally.
Why Digital Signature Validation in PDF Matters for Trust and Compliance
Validation protects documents from tampering, identity fraud, and unauthorized post-signing edits risks. It is required across legal, financial, academic, and regulated professional environments globally. Moreover, proper digital signature validation in PDF ensures compliance, credibility, and long-term document trust.
Part 2. When and Why You Need to Validate a PDF Signature
The following situations explain when validating a PDF signature becomes necessary for secure decisions:
Signed Contracts: Validate contracts to confirm signer identity and ensure terms remained unchanged after execution. This prevents disputes by proving authenticity before approvals, payments, or long-term obligations arise.
External Documents: Verify external documents to trust sources, certificates, and compliance across organizational boundaries securely. Validation detects expired certificates or untrusted issuers before reliance or recordkeeping decisions occur.
Post Changes: Confirm document integrity by checking that cryptographic seals indicate no post-signing alterations occurred later. Opening files cannot reveal tampering because validation verifies hashes, timestamps, and trust chains.
Compliance Audits: Validate audit documents to meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate verified signing practices clearly. This supports inspections by providing proof of integrity, authenticity, and signer accountability.
Part 3. How Online PDF Signature Validation Works
Online PDF signature validation is designed for quick, accessible checks without installing desktop software. When users validate a signature in a PDF online, the tools upload the document and scan the embedded signature data. This process focuses on surface-level verification rather than deep forensic or compliance analysis. It helps users quickly assess whether a signature exists and appears technically intact.
What Online Tools Typically Check
Signature Presence: Confirms whether a digital signature exists within the PDF structure.
Basic Certificate Status: Checks certificate expiration, issuer recognition, and basic validity indicators.
What Online Validation Usually Cannot Show
Full Certificate Chain Details: Online tools rarely display root trust paths or intermediate certificate relationships.
Detailed Modification History: They cannot fully trace document changes before and after signing events.
Setting the Right Expectations
Online validation is suitable for quick checks and low-risk document reviews.
It should not replace desktop tools for legal, compliance, or audit-critical workflows.
Part 4. How to Validate a Digital Signature in a PDF Online (General Steps)
The steps below outline a simple, tool-agnostic method used by most online validation platforms:
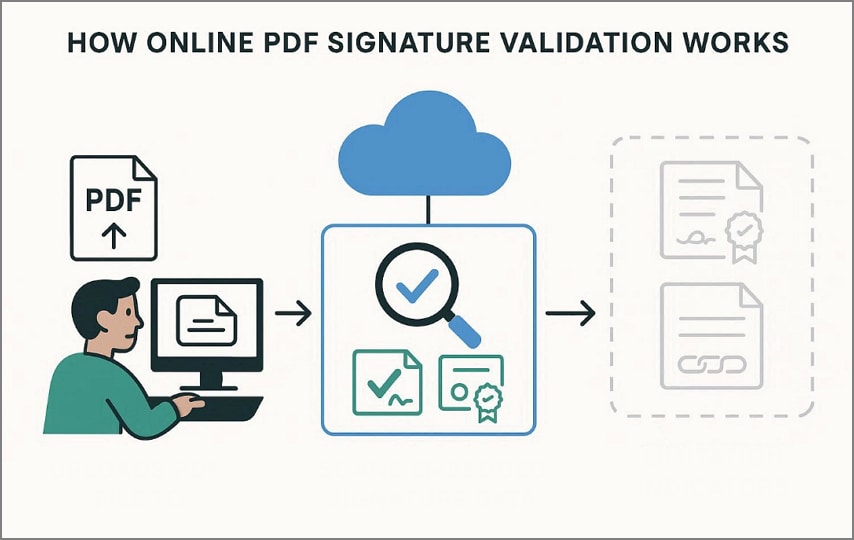
Step 1
First, upload the signed PDF file to a trusted online signature validation tool securely now.
Step 2
Next, view the displayed signature status indicating valid, invalid, or unknown results clearly on screen.
Step 3
Afterwards, review any warnings or messages explaining certificate problems or document integrity issues carefully shown.
Step 4
Lastly, download the file for records or close the session after completing validation securely online.
Note: Validation results depend on certificate trust status and whether document integrity remains intact.
Part 5. How to Verify a PDF Signature Using Adobe Reader
Adobe Acrobat Reader is often treated as a reference standard for signature verification worldwide. Many organizations rely on it because Adobe defines and maintains core PDF security specifications. As a result, Adobe signature verification is widely trusted for legal, academic, and compliance workflows. Adobe uses embedded certificates, trust lists, and cryptographic checks to evaluate signature integrity.
How Adobe Signature Verification Works
When a signed PDF is opened, Adobe automatically detects digital signatures. It checks whether the document changed after signing and verifies certificate trust chains. Warnings, trust icons, and timestamps help users interpret results clearly and consistently. Adhere to the steps below to verify a signature in Adobe Reader:
Step 1
First, load the signed PDF file in Adobe Acrobat Reader on your system. After that, choose the "Signature panel" or Signature field display within the document.
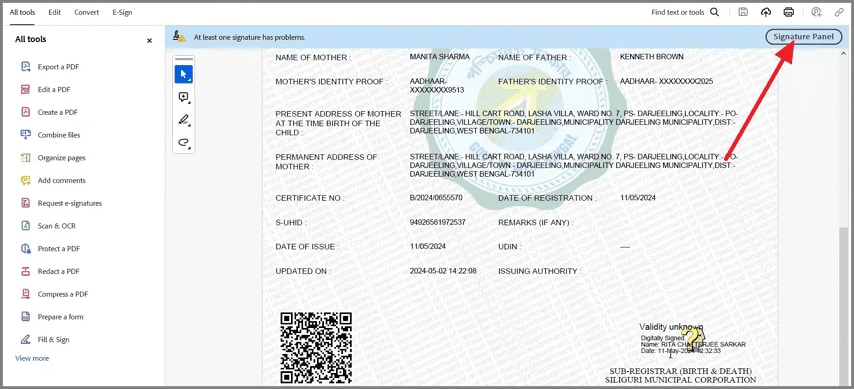
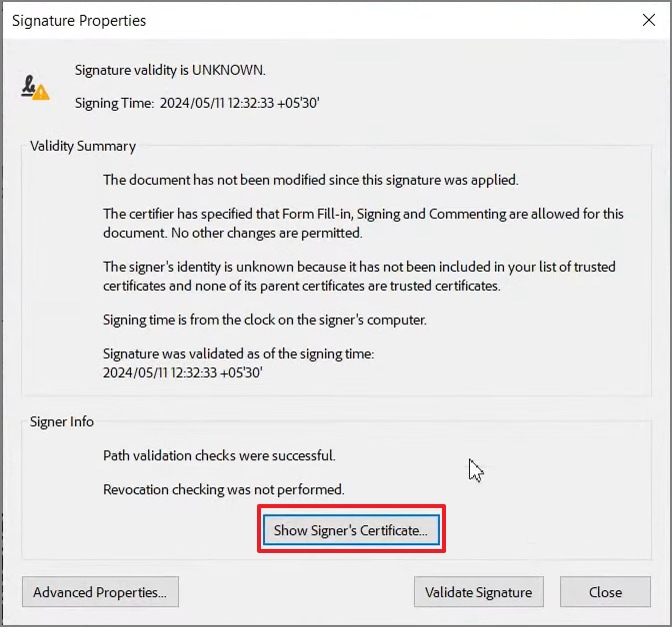
Step 2
After that, select "Signature Properties" to view signing time, integrity status, and validation summary. Here, Adobe explains whether the document changed and why the signer is trusted or unknown.
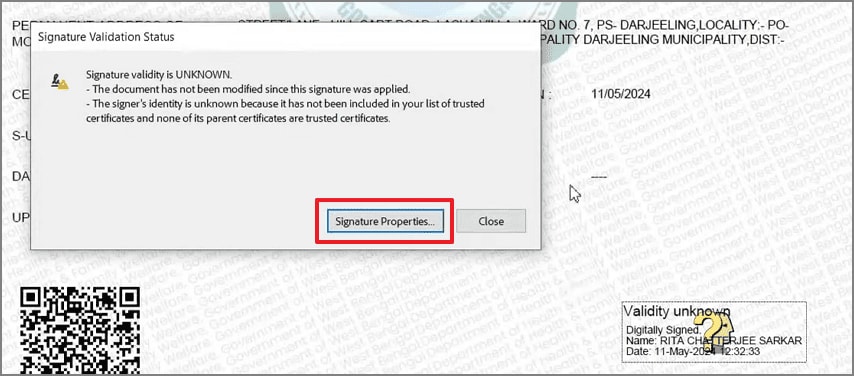
Step 3
Next, click "Show Signer's Certificate" to inspect trust settings and certificate paths. This step confirms certificate trust, revocation checks, and explains any unknown status clearly.
Part 6. What "Valid," "Invalid," and "Unknown" Signature Statuses Mean
Understanding signature status results is essential before trusting or rejecting any digitally signed PDF, so review the points below:
Valid Signature: A valid signature confirms that the document remained unchanged after signing and that integrity is preserved. It also indicates the certificate is trusted and recognized by the validation tool system.
Invalid Signature: A signature is invalid when the document has been modified, or signature integrity has been compromised. It may also indicate certificate expiration, revocation, or a mismatch during verification checks.
Unknown Signature: An unknown signature appears when the system does not trust the certificate. This often happens when root certificates are missing or not preinstalled locally.
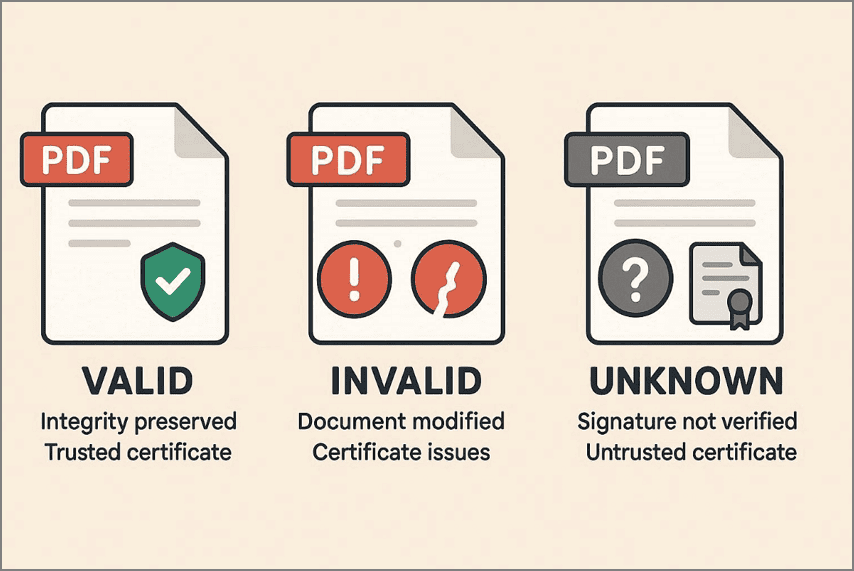
Note: Different tools show different results because trust stores, certificate databases, and validation depth vary.
Part 7. Common Reasons a PDF Signature Fails Validation
PDF signature validation failures usually stem from trust and integrity issues rather than technical file errors. Understanding the following causes helps users interpret warnings correctly instead of assuming the PDF itself is broken:
Document Changes: Any modification after signing immediately breaks the cryptographic seal protecting the document. Validation fails because the file no longer matches the original signed content state.
Certificate Expiry: Digital certificates expire or become revoked to maintain security standards over time. Even unchanged documents fail validation when the signer's certificate is no longer valid.
Trust Chain: A missing or unrecognized certificate chain prevents establishing signer trust. This often results in an unknown validation status despite correct signing procedures initially.
Timestamp Errors: Untrusted or missing timestamps block confirmation of certificate validity during signing. Without timestamps, long-term verification becomes unreliable across systems and tools.

These issues reflect trust and integrity failures rather than PDF formatting or compatibility concerns. Accurate digital signature validation in professional workflows depends on certificates, timestamps, and verification trust models.
Part 8. How to Validate a PDF Digital Signature in Detail Using PDFelement
Online tools and viewers are useful for quick checks, but they show limited information. On the other hand, desktop PDF editors like Wondershare PDFelement enable deeper digital signature validation in PDF by analyzing complete signature metadata locally. This allows users to review trust status, document integrity, and timestamps without uploading sensitive files online.
Why Desktop Editors Enable Deeper Validation
Desktop editors analyze the entire signature structure instead of surface indicators only. They use local trust stores, certificate paths, and timestamps for accurate verification. This approach supports the detailed review required for legal, academic, and compliance workflows.
What does PDFelement Allows Users to Check?
Signature Status: PDFelement clearly shows whether the signature is valid, invalid, or untrusted. This helps users immediately understand the document's verification state.
Certificate Details: Users can view signer identity, issuer information, and certificate validity periods. These details explain who signed the document and under what authority.
Document Integrity: The editor confirms whether the PDF was modified after signing. Any post-signing changes are flagged clearly for user awareness.
Timestamp Information: PDFelement displays signing time and timestamp validation results. This helps confirm whether the certificate was valid at signing time.
How PDFelement Fits Into Verification Workflows
PDFelement complements online tools and Adobe Reader by offering deeper visibility locally. It enables digital signature validation in PDF without file uploads or privacy risks. This makes it a practical choice when transparency, security, and detailed verification are required.
Part 9. Online vs. Adobe vs. Desktop Validation: What's the Difference?
Understanding validation depth helps users choose the right method for PDF signature verification across different workflows.
| Validation Method | Detail Level | What It Checks | Best Use Cases | Limitations |
| Online Tools | Low | Signature presence, basic certificate status | Quick checks, low-risk documents, one-time reviews | Limited trust details, no full certificate chains |
| Adobe Reader | Medium | Signature validity, document integrity, certificate trust | Legal review, standardized verification, reference checks | Moderate detail, limited transparency into trust logic |
| Desktop Editors (e.g., PDFelement) | High | Full signature status, certificates, timestamps, and modification checks | Compliance, audits, sensitive or regulated documents | Requires installation, more user interaction |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How do I validate a digital signature in a PDF online?
Upload the signed PDF to an online validator to check the signature status securely. The tool analyzes integrity and certificate trust without installing desktop software locally first. -
Why does my PDF signature show as invalid?
PDF signatures appear invalid when documents change, or certificates expire unexpectedly during validation. Invalid status reflects trust or integrity problems rather than file format issues alone. -
Is Adobe Reader enough for signature verification?
Adobe Reader provides reliable baseline checks for most standard digital signature validation needs. However, complex compliance reviews may require deeper certificate inspection tools for auditors specifically. -
Can a PDF signature be valid but untrusted?
Yes, a signature can be cryptographically valid but not trusted locally by systems. This happens when root certificates are missing from trust stores on receiving devices. -
Do I need to upload my file to verify a PDF signature?
Online verification usually requires uploading files to external servers temporarily for analysis purposes. Desktop tools verify signatures locally without uploading sensitive documents to third-party platforms online.
Conclusion
To conclude, knowing how to validate a signature in a PDF online helps users confirm document authenticity efficiently. Online tools support quick checks, while Adobe Reader provides a trusted baseline. However, complex or sensitive documents require deeper inspection of certificates and integrity. For full transparency without uploading files, PDFelement offers a reliable desktop solution for secure, accurate signature validation.

 G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |
G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |  100% Secure
100% Secure



