In this article
- Why People Confuse Digital Signatures and Digital Certificates
- What Is a Digital Certificate?
- What Is a Digital Signature?
- Digital Signatures vs Digital Certificates: The Core Differences
- What Is a "Digital Signature Certificate"?
- How Digital Certificates and Digital Signatures Work Together?
- Digital Signatures and Certificates in PDF Documents (Real-World Example)
- What Is a DSC Certificate?
- What Is a DGFT Certificate?
- When Do You Need a Digital Certificate vs Just a Signature?
- Common Misconceptions About Digital Signatures and Certificates
Online documents need strong security to protect identity, integrity, and trust. Many users confuse digital security terms, which leads to risky mistakes during verification. This confusion becomes critical when approvals, contracts, and sensitive records move online. That is why a clear understanding helps organizations avoid compliance issues and operational delays.
Moreover, digital signatures vs. digital certificates explain how authentication, encryption, and trust frameworks differ. Each technology serves a purpose within secure communication and document validation. So, choosing the correct method improves legal validity, readiness, and digital security. Understanding these differences helps businesses build safer workflows and stronger user confidence.
Part 1. Why People Confuse Digital Signatures and Digital Certificates
Before explaining the technical differences, it helps to understand where confusion actually begins.
Shared Workflows: Digital signatures and certificates appear together during secure document processes. Since users see both simultaneously, confusion between digital signatures and digital certificates is common.
Interchangeable Language: Platforms often use signing and certification terms loosely without technical clarification. This casual wording makes both technologies sound identical to everyday users.
Misleading Terminology: The phrase "digital signature certificate" combines two separate security concepts incorrectly. This mixed wording convinces users that certificates sign documents, which is inaccurate.
Forced Usage: Many systems require digital actions without explaining the security tools involved. Users complete tasks successfully yet never understand what actually protects them.

Part 2. What Is a Digital Certificate?
A digital certificate is an electronic credential that proves identity in online communication. It links an individual, organization, or system to a verified public key. Issued by trusted Certificate Authorities, it enables secure encryption, authentication, and trust. In simple terms, "what is digital certificate" often refers to a digital ID used online. Many users also call it a DSC certificate in legal or signing contexts.
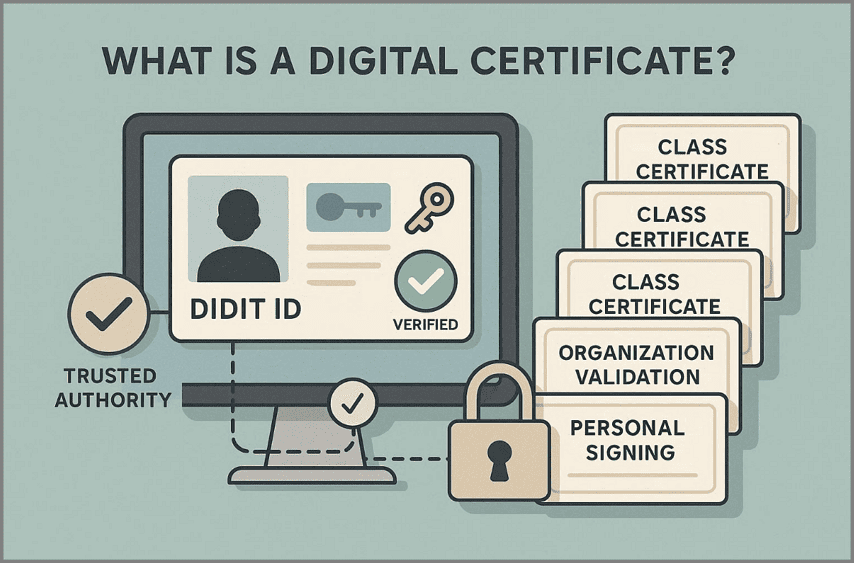
Common Digital Certificate Types Used for Signing
Class 1 Certificate: Used for basic email verification and low-risk digital identification purposes.
Class 2 Certificate: Confirms personal or organizational identity for document signing and filings.
Class 3 Certificate: Provides the highest trust level for legal, financial, and regulatory digital signatures.
Organization Validation Certificate: Verifies business identity before enabling secure document signing workflows.
Personal Signing Certificate: Confirms individual identity for contracts, approvals, and secure document authentication.
Part 3. What Is a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is a secure action applied to a document to prove approval. It confirms who signed the document and whether the content changed afterward. In simple terms, "what is digital signature" refers to a cryptographic stamp added during signing. Unlike certificates, a digital signature is created at signing time, not stored separately.

What a Digital Signature Ensures
Signer Identity: The system verifies the signer using cryptographic keys before approval is completed.
Document Integrity: Any change after signing immediately breaks the digital signature validation.
Why a Digital Signature Is Applied to Documents
A digital signature stays attached to the document it protects. This binding ensures authenticity travels with the file wherever it goes. Without this link, trust, verification, and legal reliability would be lost.
Part 4. Digital Signatures vs Digital Certificates: The Core Differences
Understanding the difference between digital signatures and digital certificates becomes clearer when each role is broken down simply.
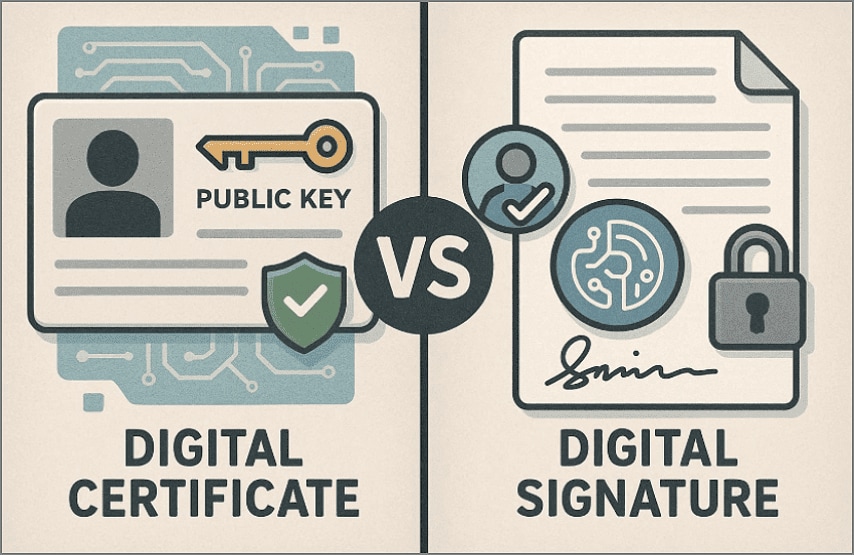
Purpose
Digital Certificate: Establishes trust by verifying identity before any secure digital action occurs.
Digital Signature: Confirms user approval and protects document content once the signing process is complete.
What It Represents
Digital Certificate: Represents a verified identity that is linked to a public cryptographic key.
Digital Signature: Indicate explicit consent and proof that a specific document was approved.
How It is Used
Digital Certificate: Operates in the background for authentication, encryption, and trust validation processes.
Digital Signature: Is applied directly to documents during controlled digital signing workflows.
Ability to Exist Alone
Digital Certificate: Can exist independently, even if not actively used for document signing.
Digital Signature: Cannot exist alone because it must always be attached to protected content.
Part 5. What Is a "Digital Signature Certificate"?
Before diving deeper, it helps to clarify this term, which often causes misunderstandings.
Why This Term Exists
The term digital signature certificate emerged because signing always requires verified identity credentials. Most digital platforms hide technical security layers, showing users only a simple signing action. As a result, certificates and signatures become merged into one simplified expression.
What People Usually Mean
When users ask, "What is a digital signature certificate?" they usually mean a certificate used to sign. They are not referring to a separate technology or a unique cryptographic mechanism. Instead, they describe the credential that enables secure digital signature creation.
What It Actually Refers To
In technical terms, "What is the digital signature certificate?" becomes clear to security professionals. It refers to a digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority after identity verification. This certificate verifies identity and provides cryptographic keys required for creating secure digital signatures. In practical use, the certificate proves who you are during secure digital interactions. The digital signature proves that you signed and confirms that the document remains unchanged.
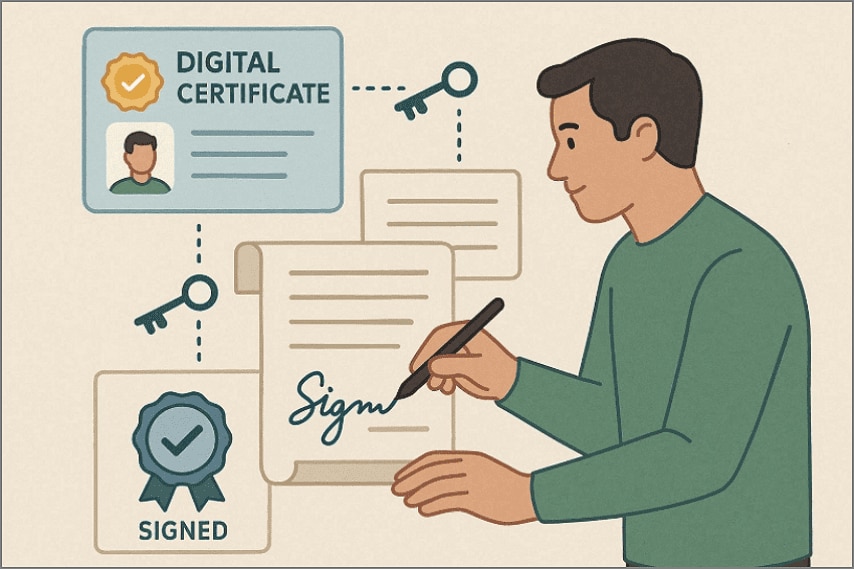
Part 6. How Digital Certificates and Digital Signatures Work Together?
To understand their relationship, it helps to follow the process in the following simple sequence:
Step 1
A digital certificate is issued to a person or organization after identity verification. This certificate acts like a trusted digital ID in online environments.
Step 2
Then the digital certificate is used to create a digital signature when approval is needed. It supplies secure keys that allow the signing action to occur safely.
Step 3
After that, the digital signature is applied directly to the document being approved or shared. This action locks the content and links it to the signer's verified identity.
Step 4
Other users check the signature using the signer's digital certificate. This process confirms who signed the document and ensures nothing was changed afterward.
In simple terms, certificates establish identity, while digital signatures protect document trust.
Part 7. Digital Signatures and Certificates in PDF Documents (Real-World Example)
PDF documents are one of the most common places where digital trust is enforced. They are used for contracts, approvals, invoices, and official records that must remain unchanged. Since PDFs are shared widely and finalized frequently, they rely heavily on digital signatures.
Why are PDFs Commonly Use Digital Signatures
The PDF file is created in such a way that it can maintain a layout and content on various devices.
The document cannot afford an opportunity to allow undetected modifications and alterations once it is signed.
The PDFs become tamper-evident and legally binding with the help of digital signatures.
How Certificates Are Used Inside Signed PDFs
A digital certificate is embedded or securely referenced during the signing process. The certificate links the signer's verified identity to the document version being signed. This connection allows long-term verification, even after the file is shared externally.
What Recipients See When Opening a Signed PDF
A visible signature indicator appears within the document interface.
The status shows whether the signature is valid, trusted, or altered.
Recipients can open signature details without technical knowledge or extra tools.
Practical Workflow Inside PDF Editors
To make the process tangible, it helps to look at how digital signing works inside a real PDF editor. In PDF editors such as PDFelement, digital signatures vs. digital certificates are handled through a guided workflow. These editors are commonly used when PDF documents move from drafting to formal records. Contracts, approvals, and official files typically require both identity verification and content protection.
Instead of exposing cryptographic complexity, the signing process is structured into controlled steps. So, understanding the following workflow helps clarify how certificates and signatures operate together in practice:
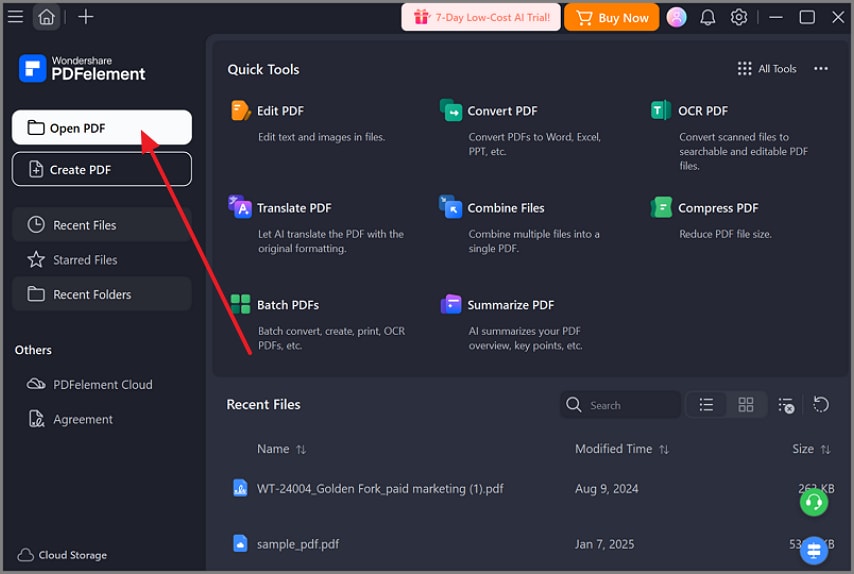
Step 1Import a Digital Certificate
Users can import an existing digital certificate into the editor's certificate management area. This step prepares verified identity credentials before any document is signed.
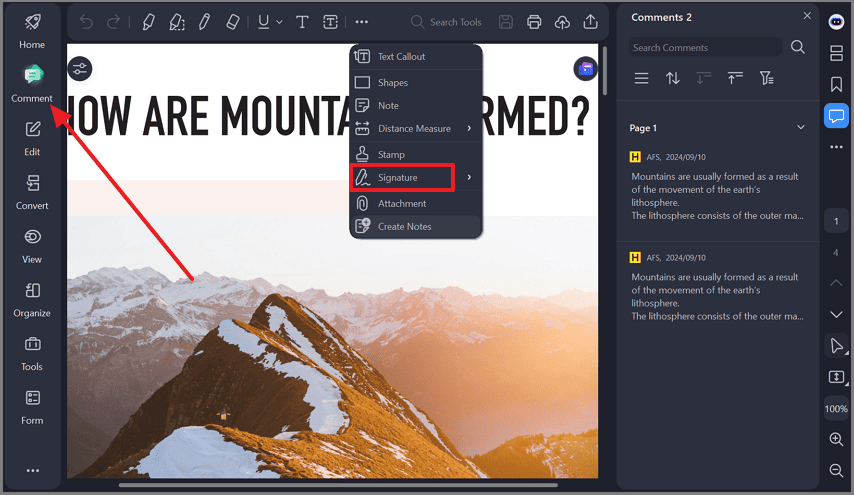
Step 2Apply the Certificate as a Digital Signature
After opening a PDF, the imported certificate is used to create a digital signature. The signature is applied directly to the document at a selected location.
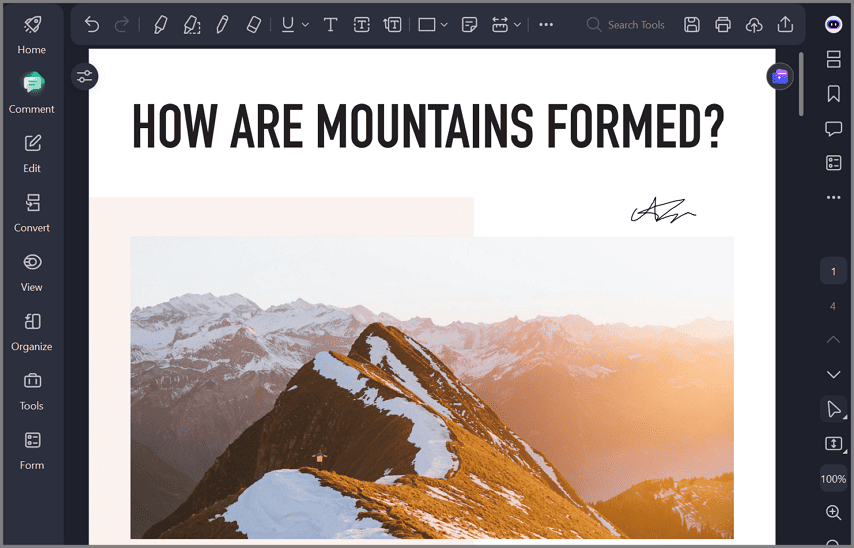
Step 3View Certificate Details During Verification
When a signed PDF is opened, signature status information is displayed. Recipients can view certificate details such as issuer, validity period, and trust status.
Part 8. What Is a DSC Certificate?
A DSC certificate stands for Digital Signature Certificate, a legally recognized digital certificate used for secure signing. When people ask "what is DSC certificate," they are referring to a government-approved identity credential. It is issued to individuals or organizations to authenticate identity during regulated digital transactions.
Where DSC Certificates Are Commonly Required
DSC certificates are widely used in compliance-driven and region-specific environments. They are commonly required for government portals, tax filings, corporate submissions, and regulatory forms. In many jurisdictions, digital filings are not accepted without a valid DSC certificate attached.
How DSC Fits into the Certificate–Signature Relationship
A DSC certificate does not act as a signature by itself. Rather, it serves as the validated identity applying to the generation of digital signatures. The certificate is used to determine the identity of the signer, and the digital signature is used to determine what was signed. They work together to guarantee the validity of the law, identity verification, and document integrity.
Part 9. What Is a DGFT Certificate?
A DGFT certificate is a digital credential used to access and authenticate users on trade-related government portals. When users ask "What is a DGFT certificate?", they usually refer to the authorization required for export and import activities. It is issued for use with platforms managed by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade.

How DGFT Certificates Relate to Digital Certificates and Signatures
A DGFT certificate does not function as a digital signature on its own. Instead, it works with a digital certificate to verify user identity on government systems. Digital signatures are then used to approve and submit official trade documents securely.
Common DGFT Certificate Use Cases
Export Import Code Access: Used to register, update, or manage IEC details on official trade portals.
License Applications: Required for applying for import, export, or restricted goods licenses online.
Trade Compliance Filings: Enables secure submission of declarations, forms, and compliance documents.
Government Portal Authentication: Confirms user identity when accessing DGFT-managed digital services.
Part 10. When Do You Need a Digital Certificate vs Just a Signature?
Before choosing a signing method, it helps to compare when each option is appropriate.
| Decision Factor | Digital Certificate Required | Simple Electronic Signature Enough |
| Identity Verification Level | Requires high-trust identity verification issued by a trusted authority | Relies on basic user authentication or platform verification |
| Regulatory or Government Use | Mandatory for government portals and regulated submissions | Generally not accepted for statutory filings |
| Legal Accountability | Provides strong non-repudiation and verifiable audit trails | Indicates user intent with limited legal assurance |
| Document Risk Level | Used for high-value, sensitive, or legally binding documents | Suitable for low-risk or internal documents |
| Verification Method | Uses cryptographic keys tied to a verified identity | Uses system logs, emails, or user confirmation |
| Long-Term Validation | Supports long-term verification even after document sharing | Often limited to the signing platform's availability |
| Typical Use Cases | Compliance filings, financial documents, legal agreements | Internal approvals, acknowledgements, and basic consent forms |
Part 11. Common Misconceptions About Digital Signatures and Certificates
Many users misunderstand how digital signatures and certificates actually work. The following myths often lead to incorrect assumptions about document security, legal validity, and trust. Clarifying them helps users avoid risky decisions in regulated or professional workflows:
"A digital signature is just an image."
This is one of the most common misconceptions among people. A real digital signature is not a scanned image or handwritten mark placed on a document. Instead, it is a cryptographic process that locks the document's content and links it to a verified identity. If the document changes after signing, the signature immediately breaks, showing tampering. An image-based signature has no built-in security, identity verification, or tamper detection.
"Certificates and signatures are the same thing."
Digital certificates vs digital signatures serve different but connected roles. Digital certificates and digital signatures are related tools, but they perform distinct security roles. Certificates confirm signer identity through trusted authorities, while signatures secure document approval.
"If a PDF opens, the signature must be valid."
Opening a signed PDF alone does not confirm that the signature remains valid. Signatures may appear visible despite expiration, revocation, untrusted issuers, or document alterations. Understanding these distinctions prevents compliance issues and ensures documents meet real verification standards.
Why Clearing These Myths Matters
When convinced that these misconceptions are capable of producing actual issues, including declined documents or compliance concerns. People make safer choices when they know how certificates and signatures really work. Such transparency enhances the security of documents and also makes sure that signed PDFs are not only convincing to the eye but also authentic.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between a digital signature and a digital certificate?
A digital certificate ensures the identity of the signer, whereas a digital signature secures the document once it has been signed. Trust comes first, and on that trust, signatures are used to sanction content in a secure and legal way. -
Is a digital signature the same as a DSC?
No, a digital signature is not identical to a DSC, which represents the certificate itself. A DSC provides identity credentials, while a digital signature securely signs documents electronically. -
Do I need a digital certificate to sign a PDF?
Yes, a digital certificate is required to create a cryptographically valid digital signature file. Without a certificate, you can only add visual signatures, lacking security controls or verification. -
What does "digital signature certificate" actually mean?
The term digital signature certificate informally describes a certificate used for signing documents securely. It does not represent a separate signature type, but the identity credential behind signatures. -
How can I see certificate details in a signed PDF?
Open the signed PDF and use signature properties to view the embedded certificate information details. PDF viewers display issuer, validity dates, and trust status within verification panels clearly shown.
Conclusion
To conclude, understanding the digital signature vs. digital certificates helps organizations avoid security mistakes and compliance risks. Certificates confirm verified identity, while signatures protect documents against tampering after approval. Knowing the difference improves trust, legal acceptance, and long-term confidence across workflows. For everyday use, PDFelement offers practical tools for signing, verifying, and managing certificates securely.

 G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |
G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |  100% Secure
100% Secure



