Imagine working with hundreds of scanned pages or image-based PDFs and realizing you are unable to copy or search any text inside them. It's frustrating when you just need to extract information quickly or build an automated workflow. DeepSeek changes that by turning scanned documents into machine-readable text using its advanced optical character recognition technology.
Whether you want to process long PDFs, connect through the DeepSeek OCR API, or explore its GitHub resources, this guide will walk you through everything. You'll also discover a simpler, no-code OCR alternative for instant PDF cleanup and multilingual text extraction.
In this article
- Quick Answer
- What Is DeepSeek OCR?
- DeepSeek OCR API — How to Call It
- DeepSeek OCR on GitHub — Clone & Run Locally
- Using DeepSeek OCR for PDFs
- Ollama + DeepSeek OCR (Local-First idea)
- A Faster Path for Everyday Teams: PDFelement (No-Code PDF OCR & Cleanup)
- DeepSeek OCR vs PDFelement vs Classic OCR — When to Use What
- Step-by-Step Playbooks (Copy-ready)
- Known Considerations (Accuracy, Security, Availability)
Part 1. Quick Answer
DeepSeek-OCR is open-source software that uses "optical compression" to process huge documents with ultra-long context. It's best for developers who need large-scale extraction and is available on GitHub with full API docs online. For most teams requiring multilingual OCR with a simple GUI, PDFelement's OCR and Enhance Scan features are more practical. Choose DeepSeek for token efficiency and pick PDFelement for everyday PDF text extraction and cleanup via user-friendly tools.
Part 2. What Is DeepSeek OCR?
This system transforms documents into compact visual tokens and enables ultra‑efficient long‑context processing for AI. It preserves complex layout structure, reduces token costs, and outputs analysis‑ready text. To help language models handle longer documents in a single pass, it compresses pages in a visual presentation. Supports multilingual and mixed‑format documents across research, enterprise, and developer workflows. Let's look at some key capabilities and benefits that this tool offers.

- Optical Compression Engine: Converts pages into compact visual tokens so language models process much longer contexts.
- 10× Token Reduction: Reduces token counts by roughly ten times while sustaining strong recognition across diverse document layouts.
- High‑Throughput Processing: Delivers high throughput on multi‑page workloads using optimized tiling, batching, and caching strategies.
- Dynamic Modes/Resolution: Adapts resolution and views for scientific PDFs, invoices, tables, charts, and diagram‑heavy files.
- Structured Outputs: Produces structured Markdown or JSON to preserve tables, lists, charts, and overall document hierarchy.
You can explore the full research overview and code samples in DeepSeek's official GitHub repository and technical papers.
Part 3. DeepSeek OCR API — How to Call It
The DeepSeek OCR API allows developers to integrate advanced document processing into their workflows. It is easily accessible to developers familiar with OpenAI SDKs, without requiring an understanding of a completely new API format, thanks to its OpenAI compatibility. Users can send scanned pages, images, or PDFs and receive structured text output with this API. The results are ready for AI workflows, knowledge bases, or research pipelines.
API Format and Request Structure
The API uses a standard HTTP request structure compatible with OpenAI-style SDKs. A typical request includes:
- Endpoint URL: The API endpoint where you send requests to process documents, e.g., https://api.deepseek.com/v1/ocr.
- Headers: Include your Bearer token and any required authentication details for access.
- Input File: Provide either an uploaded image, a PDF page, or a public URL for OCR processing.
- Optional Parameters: Specify language, layout mode, resolution, or other preferences for better results.
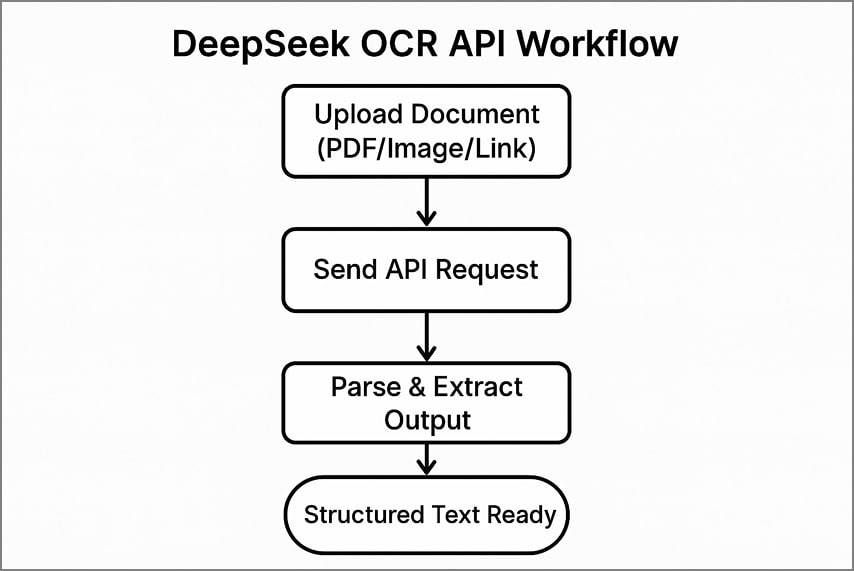
Typical API Workflow
Using the DeepSeek OCR for API involves 3 clear steps to process documents and extract structured text.
- Upload your document to the API by sending a file, a PDF page, or a public link.
- Send the API call with your authentication headers and chosen options for processing.
- Parse the returned JSON or text to extract recognized content, layout details, and visual tokens accurately.
Rate Limits, Availability, and Reliability
While the API is powerful, developers should be aware of some operational considerations:
- Service Availability: The API has shown occasional fluctuations in uptime, so plan for potential downtime or slower response times in production.
- Rate Limits: When dealing with large-scale processing, you may hit a limit on the daily or per-minute rate, thus taking retries as a way of backoff timing to keep the continuity.
- Error Handling: Always check responses for errors and handle exceptions gracefully to avoid failed workflows in production.

Part 4. DeepSeek OCR on GitHub — Clone & Run Locally
We will explore how you can install DeepSeek OCR GitHub locally by setting up the Python environment after cloning the repository.
Accessing the Repository
DeepSeek OCR is available as an open-source project on GitHub that provides developers with full access to its architecture and scripts. The repository includes environment configuration files and documentation for deployment or customization. Distributed under a permissive license, it supports both research and production use. The project has an active community that frequently contributes to bug fixes and workflow improvements for local deployment.

Local Setup (Step-by-Step Commands)
To install DeepSeek OCR locally, simply clone the repository and prepare your Python setup:
"git clone https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-OCR
cd DeepSeek-OCR
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
pip install -r requirements.txt"
The tool is compatible with Python version 3.9 or later releases. Model weights can be downloaded automatically on first use or manually via links in the README file.
GPU Requirements and Performance Notes
DeepSeek OCR can run on a CPU, though a CUDA-capable GPU is highly recommended for processing high-volume OCR workloads. In in-house comparisons, there is the capability of 5-10 times faster throughput on the multi-page PDFs or complicated document layouts using GPU acceleration. For optimal performance, make sure your NVIDIA drivers, CUDA, and PyTorch versions are updated.
Running Inference on PDFs
After completing the setup, test a sample PDF file using the following command:
"python infer.py --input sample.pdf --output output.json"
Each page is rendered as an image and processed through the VL2 vision pipeline to detect text and retain layout. The structured JSON or Markdown output integrates into RAG or Ollama-based local LLM workflows.
Part 5. Using DeepSeek OCR for PDFs
Let's look at how developers commonly use DeepSeek OCR PDF methods to extract accurate text and layout data from scanned or digital documents.
Methods Developers Use Today
For PDFs, there are two practical ways teams run DeepSeek today, depending on quality, cost, and latency trade‑offs.
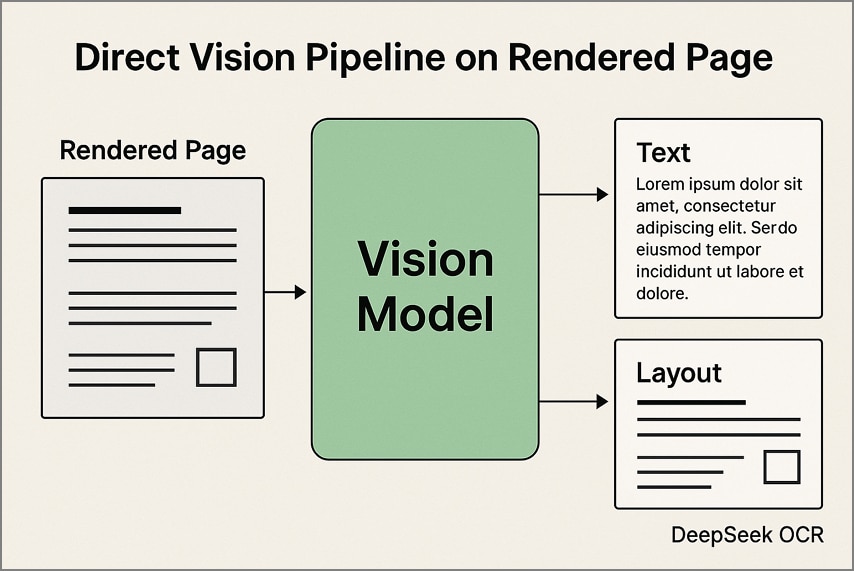
1. Direct Vision Pipeline on Rendered Pages
In this approach, every PDF page is converted into an image at a fixed resolution before being processed through DeepSeek OCR. The model extracts both text and layout details directly from the visuals, maintaining tables, columns, and diagrams in their original structure. This method is particularly effective for scanned documents and visually complex layouts.
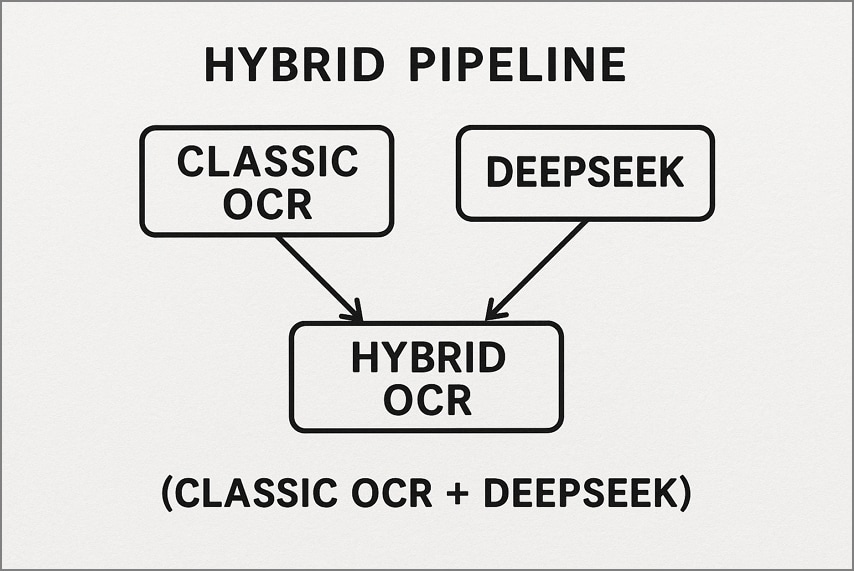
2. Hybrid Pipeline (Classic OCR + DeepSeek)
Here, a traditional OCR tool such as Tesseract handles simple, high-quality pages first to produce quick text output. Only the more complex or noisy pages are passed to DeepSeek OCR for deeper layout reconstruction and semantic understanding. This workflow reduces cost and latency while still achieving premium accuracy on difficult documents.
Edge Cases
Some documents are harder to process than standard text pages, so it's important to handle edge cases carefully for the best OCR accuracy.
- Multi‑Column Magazines/Newspapers: Enforce correct column order with post-OCR line grouping, prefer 300 DPI, tile per column for dense pages.
- Stamps/Watermarks/Seals: Mask or separate overlays before OCR to avoid false text and wrong merges, then reinsert afterward.
- Skew/Rotation: Deskew pages first, detect orientation reliably, then run OCR again on pages that were rotated.
- Low‑DPI Scans: Upsample by about 1.5-2 times and sharpen, otherwise prefer rescanning at higher DPI.
- Tables and Forms: Run a table detector or a header alignment step to fix split cells, then validate totals and key fields.
- Fonts/Math/Code: Use higher resolution tiles for equations, code blocks, and very small fonts, and preserve monospacing with code fences.
Why Post‑Processing Matters
Post-processing is the simple clean-up after text extraction, so the result reads correctly. It fixes mixed columns, broken tables, messy headings, and stamps accidentally read as words. If something looks wrong, re-run that page at higher quality and check totals, dates, and IDs.
Part 6. Ollama + DeepSeek OCR (Local-First idea)
It is a lightweight framework that runs large language models entirely on your computer, with a simple local API and CLI. Ollama DeepSeek OCR lets you process scanned documents and PDFs end‑to‑end on your machine to avoid cloud dependencies and preserve structure in outputs like Markdown or JSON.
Community Integration and Examples
In this section, we will explore community projects that combine DeepSeek OCR with Ollama models for local document processing, extraction, and analysis.
- Streamlit OCR Studio: A Streamlit dashboard ingests PDFs and images and runs DeepSeek OCR for structured text. Then, this model answers user questions over the extracted content locally.
- Markdown Extractor + Ollama QA: Image‑to‑Markdown utility is used to convert page images into clean Markdown for downstream use. An Ollama chat model summarizes documents and extracts key fields from PDFs and scanned images.
- Local Analyzer + Ollama API: A watch‑folder service OCRs new files with DeepSeek as they arrive. It exposes a local Ollama endpoint for search, Q&A, redaction, and workflow automation.
Why Local Orchestration Helps
After running Ollama with DeepSeek OCR locally, let's explore some key advantages of this setup.
- Keep documents on-device to meet strict data policies and reduce breach exposure during audits.
- Run entirely without internet in secure labs and air‑gapped networks for compliance testing.
- Avoid network delays, control batching and caching locally, and stabilize throughput for large PDFs.
Part 7. A Faster Path for Everyday Teams: PDFelement (No-Code PDF OCR & Cleanup)
Many users without technical experience often struggle to extract text from scanned PDFs or image-based documents. Apart from DeepSeek OCR, they search for tools that offer easy OCR processing, document cleanup, and quick text extraction without technical knowledge. This is where PDFelement comes in, which simplifies PDF extraction with no-code OCR and helps teams convert documents into searchable formats in seconds.
Unlike other tools, users can also underline, add a watermark, insert a background, and chat with AI regarding their PDFs. PDFelement provides you with up to 20GB of storage to save your data within this tool and share directly via social media platforms. Furthermore, to make the targeted area editable, it offers an "OCR Area" option for selecting specific parts of a document.
Ultimate Guide for No-Code PDF OCR in PDFelement
After learning about the best PDF OCR tool for non-coders, follow this step-by-step workflow to process PDFs quickly as an alternative to the DeepSeek OCR API:
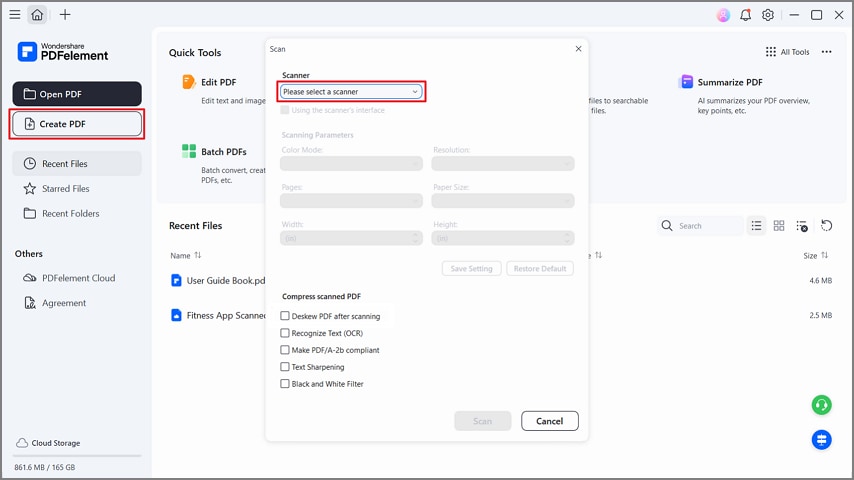
Step 1Create PDF from Scanner
Once you enter the tool, press the "Create PDF" button and select the "From Scanner" option from the drop-down menu. Next, choose your scanner and tick the "Deskew PDF After Scanning" option. This tool converts scans into searchable or editable text with desktop support.
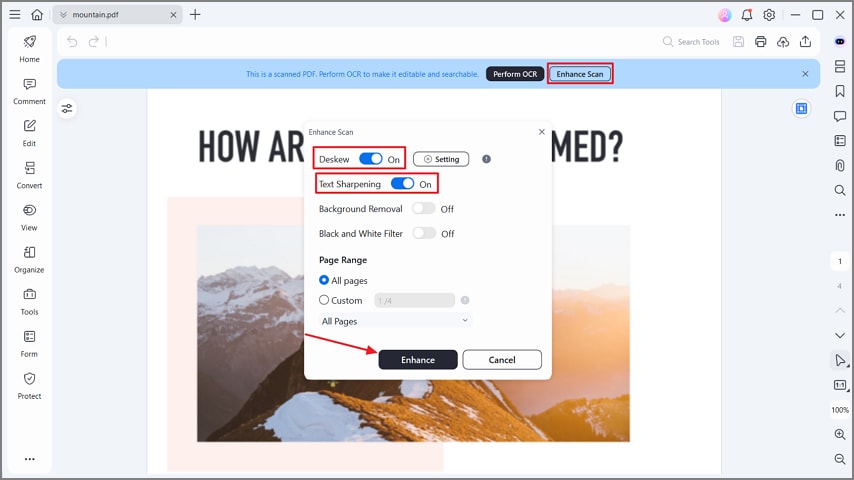
Step 2Enhance Your PDF
After the scanned PDF is created, press the "Enhance Scan" button. Next, toggle the "Deskew" and "Text Sharpening" options and hit the "Enhance" button in the pop-up window. It will sharpen the text on PDF to boost the accuracy of OCR on poor scans.
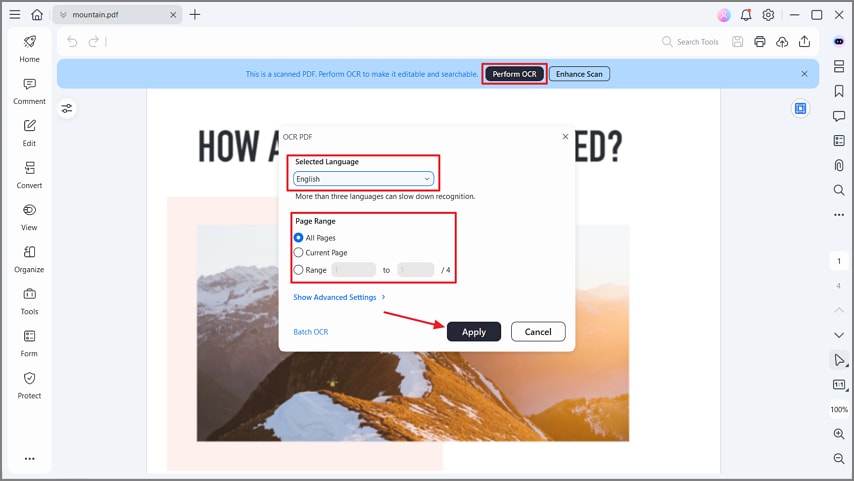
Step 3Perform Text OCR
Now, hit the "Perform OCR" button and choose the correct language. Next, select a specific "Page Range" and press the "Apply" button to begin the OCR process. This will extract the text from your PDF to make it searchable and editable for review or export.
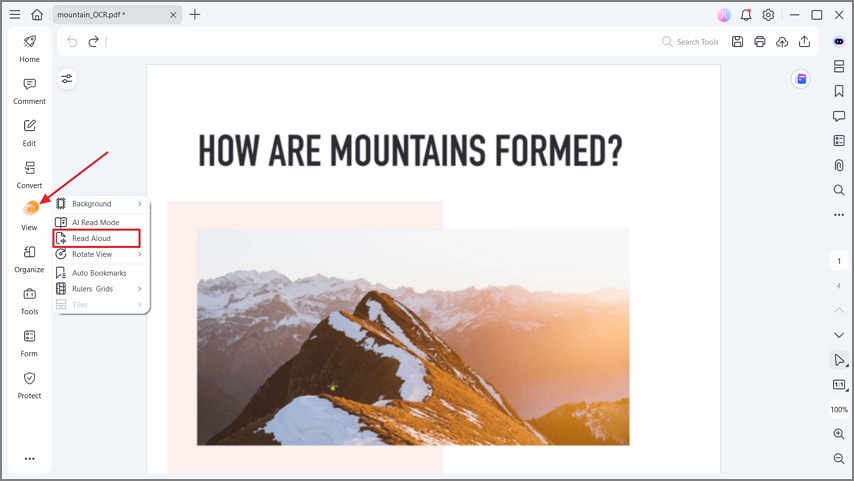
Step 4Read Aloud PDF
Once OCR is done, hit the "View" option from the left-side menu and press the "Read Aloud" option to listen to your PDF text. You can stop and pause listening at any point. This feature allows you to proofread your PDFs to pinpoint any mistakes.
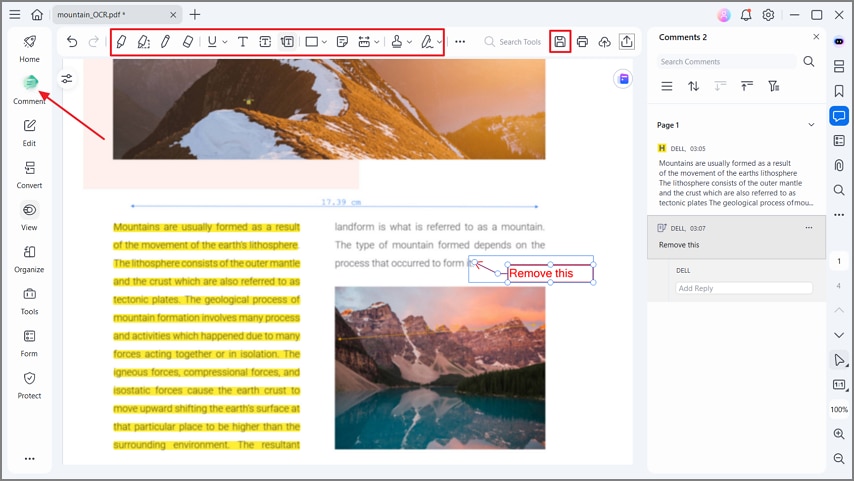
Step 5Annotate and Export PDF
Click on the "Comment" button and use the tools in the toolbar to highlight text and add comments to the PDF. Lastly, press the "Save" button to export the PDF file. The Annotate feature also helps to add stamps, draw shapes, attach stickers, and underline or strike through text for better document review.
Part 8. DeepSeek OCR vs PDFelement vs Classic OCR — When to Use What
After exploring the best DeepSeek OCR alternative, let's see what tools are ideal for different use cases and document workflows.
DeepSeek OCR
Best fit for developer pilots that demand long-context reasoning, token‑efficient RAG, and layout‑aware Markdown or JSON outputs. Expect setup and ops work, including GPU/VRAM sizing, batching or tiling choices, and occasional edge‑case tuning.
Wondershare PDFelement
A solid choice for everyday document work that needs multilingual OCR, visual Enhance Scan, annotating, and review. One‑click exports to Word or Excel streamline hand‑offs, and teams avoid coding or GPU administration.
Classic OCR Libraries
Works better on high‑volume throughput when layouts are simple and consistent across batches. Add lightweight rules or a targeted LLM pass only on difficult pages to inject semantics without paying the cost everywhere. Look at the comparison table below to understand how each tool fits different workflows and user needs.
| Tool | Focus | Setup | Long-Context | Cleanup | Multilingual | Best For |
| DeepSeek OCR | Developer workflows, RAG | Technical | Moderate | Limited/Script | Moderate | Developers, prototyping, research, RAG pipelines |
| PDFelement | Document editing & review | No-code | High | Full GUI tools | High | Business teams, operations, compliance, archiving |
| Classic OCR | Batch processing, simple docs | Technical | Medium | Script‑based | Moderate | Batch jobs, back‑office, simple layouts |
Part 9. Step-by-Step Playbooks (Copy-ready)
Now that you understand how each tool fits different workflows, let's move to quick setup guides. The following quick playbooks show how to use DeepSeek OCR GitHub and other options for both developers and non-developers.
Devs — Try DeepSeek OCR API in 10 Minutes
- Step 1. Generate an API key from "Account" or "API Keys" and set "DEEPSEEK_API_KEY".
- Step 2. Prepare POST to "/v1/chat/completions" with model, system prompt, and content schema.
- Step 3. Render PDF pages to PNG at fixed DPI and attach base64 in "messages".
- Step 4. Request strict JSON or Markdown, then parse the "content" field safely.
- Step 5. Validate fields, handle retries and persist to "Jobs" or "Storage".
Devs — Run from GitHub (Local)
- Step 1. "Clone" the repo on a CUDA‑ready machine and verify driver or toolkit versions.
- Step 2. Create venv, run "pip install -r requirements.txt", download "weights", set "MODEL_PATH".
- Step 3. Convert PDF to images at consistent DPI, run "infer.py --input pages --output out --format markdown".
- Step 4. Record "latency", "VRAM", and "throughput", and compare accuracy with a baseline OCR.
Non-Devs — Clean OCR for PDFs in PDFelement
- Step 1. First off, click the "Create PDF" and "From Scanner" to scan. Then, press the "Enhance Scan" button and enable "Deskew" and "Text Sharpening" options.
- Step 2. Press "Perform OCR", select "Language", choose "Editable Text" or "Searchable Text in Image", then click "Apply".
- Step 3. Use "AI Read" or "Read Aloud" to proof by listening, fix misreads you spot during playback.
- Step 4. Now, press the "Comment" button on the left panel to add "Highlights", "Comments", and "Stickers" for review.
- Step 5. Lastly, press the"Export" to save a searchable PDF for hand‑off.
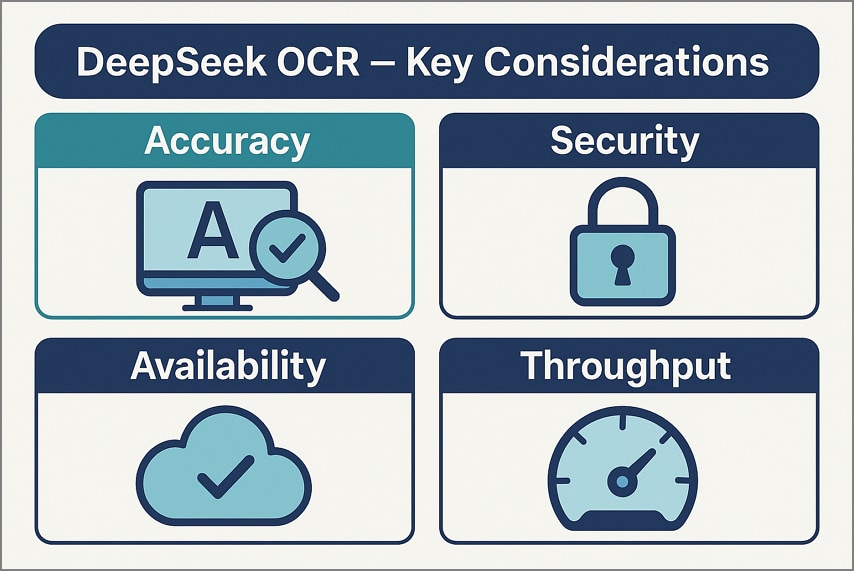
Part 10. Known Considerations (Accuracy, Security, Availability)
Before fully adopting it in production, it's important to review a few practical factors that affect how the DeepSeek OCR API performs in real-world use.
- Accuracy: Results vary with page layout and scan quality, so test performance on your own corpus first. Use representative documents, include tables and columns, and track errors like splits and merges.
- Security and Compliance: Review vendor data handling, storage, and retention, and avoid transmitting sensitive files without assessment. Add redaction before upload, restrict access, and document approvals to satisfy audits and internal policies.
- Availability and Reliability: Services can experience outages or throttling, so add retries, backoff, and resilient fallbacks locally. Monitor error rates and latency, alert on failures, and define clear operational runbooks for incidents.
- Throughput and Scaling: Treat the headline throughput as directional only, and benchmark on your hardware with fixed DPI. Measure pages per hour, GPU or CPU utilization, and costs, then rightsize batches and caching.
People Also Ask
-
What is DeepSeek OCR and why does "optical compression" matter?
DeepSeek OCR compresses page content into compact visual tokens that preserve structure and reduce token usage for downstream models. This matters because it enables larger document coverage within fixed context limits and lowers inference cost while keeping tables, lists, and layout intact. -
Where is the DeepSeek OCR GitHub repo?
The official repository provides code, examples, and references for running local inference and adapting pipelines. Clone it to evaluate outputs against your baseline OCR, customize prompts, and export Markdown or JSON for integration. -
Is there a DeepSeek OCR API and is it OpenAI-compatible?
An API exists that accepts OpenAI‑style chat requests with images or rendered PDF pages. You can request strict JSON or Markdown, then parse the response content using standard libraries and workflows. -
How do I use it on PDFs?
Render each PDF page to images at a consistent DPI, run the vision OCR, then concatenate pages and post‑process tables and lists. Alternatively, run classic OCR for raw text first, then apply DeepSeek for layout semantics, structure repair, and markdown generation. -
Can I run it with Ollama locally?
Community setups pair DeepSeek outputs with local Ollama models for Q&A, extraction, and validation. Typical patterns include Streamlit dashboards, watch‑folder processors, and lightweight document analyzers without relying on external cloud services. -
I just need to OCR a scanned PDF with multi-language support—what's easiest?
Use PDFelement for a no‑code workflow that handles deskew, denoise, and multilingual OCR reliably. Enhance the scan, choose the correct language, proof with Read Aloud or AI Read, annotate, and export a clean, searchable PDF.

 G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |
G2 Rating: 4.5/5 |  100% Secure
100% Secure



